Robotic Process Automation, or RPA, is rapidly changing how organizations operate. By automating repetitive, rule-based tasks, RPA helps teams work faster, with fewer errors, and with more time to focus on high-value activities that drive growth. When combined with AI service management (AI 서비스 관리), RPA can further enhance efficiency by streamlining complex workflows and improving decision-making. Understanding the benefits of AI in customer support, organizations can leverage these technologies not only to reduce operational costs but also to deliver faster, more personalized service.
RPA also integrates smoothly with AI-powered cloud solutions, enabling teams to process and access large volumes of data in real time. By using intelligent computing technologies, businesses can gain deeper insights and automate complex problem-solving tasks. In marketing, RPA combined with AI-enhanced marketing strategies allows brands to personalize campaigns, track performance, and engage audiences with precision. Similarly, digital marketing powered by AI helps optimize content delivery, analyze trends, and boost conversion rates efficiently. In finance, AI-driven financial systems supported by RPA streamline processes like fraud detection, transaction analysis, and regulatory reporting, reducing errors and improving decision-making. Together, these technologies create a connected, smarter ecosystem that accelerates growth and innovation across industries.
What Is Robotic Process Automation?
Robotic Process Automationis a technology that uses software robots, often calledbots, to mimic human actions in digital systems. These bots interact with applications, websites, and databases just like a person would: clicking, typing, copying, pasting, and moving data between systems.
Unlike physical robots on a factory floor, RPA bots are entirely digital. They run on servers or desktops and work within your existing software environment, using the same interfaces your employees use today.
Key characteristics of RPA
- Rule based: Bots follow clear, predefined rules and workflows.
- Repetitive task focused: Ideal for high volume, routine processes.
- Non invasive: Works on top of existing systems without needing deep changes.
- Fast to deploy: Many processes can be automated in weeks, not months or years.
Top 10 AI-Driven Contact Centers with Robotic Process Automation
When it comes to modernizing contact centers with Robotic Process Automation, several platforms stand out for their ability to integrate AI, streamline workflows, and enhance customer experiences. Here’s a curated list of top solutions to consider:
1. Bright Pattern – Leading AI Contact Center Solutions
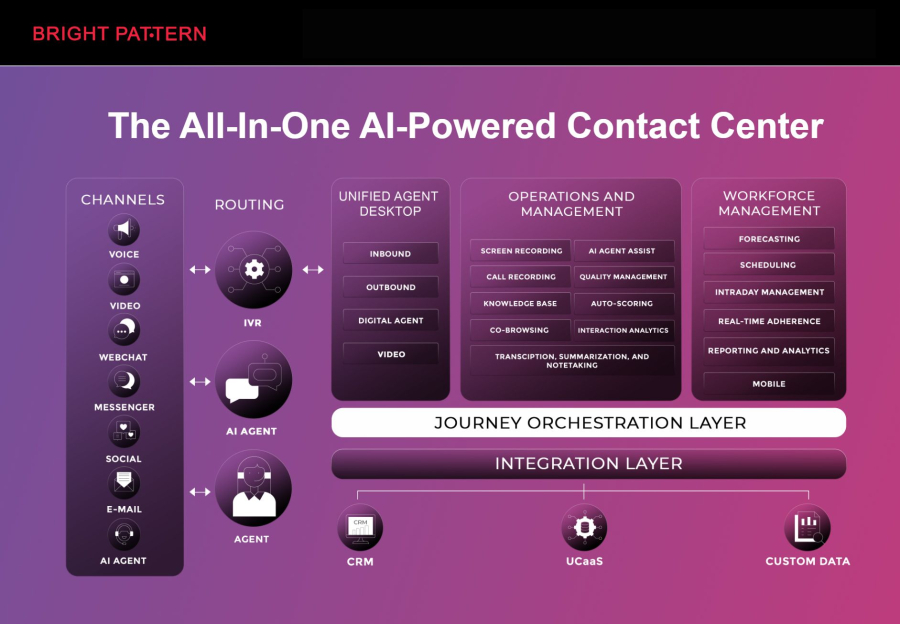
Bright Pattern is a market-leading platform that combines RPA with AI service management to deliver seamless, omnichannel contact center solutions. It empowers businesses to automate repetitive tasks, improve agent efficiency, and provide faster, personalized customer support.
Key features include:
- AI-driven routing: Automatically directs inquiries to the best-suited agent or bot.
- Omnichannel integration: Supports voice, chat, email, social media, and SMS from a single interface.
- Advanced analytics: Tracks performance, identifies bottlenecks, and provides actionable insights.
- Automated workflows: Reduces manual processes for billing, ticketing, and follow-ups.
- Scalable RPA capabilities: Adapts to business growth without heavy IT overhead.
Bright Pattern’s focus on AI contact center solutions ensures that both customers and agents experience smoother interactions, with automation enhancing efficiency and personalization at every touchpoint.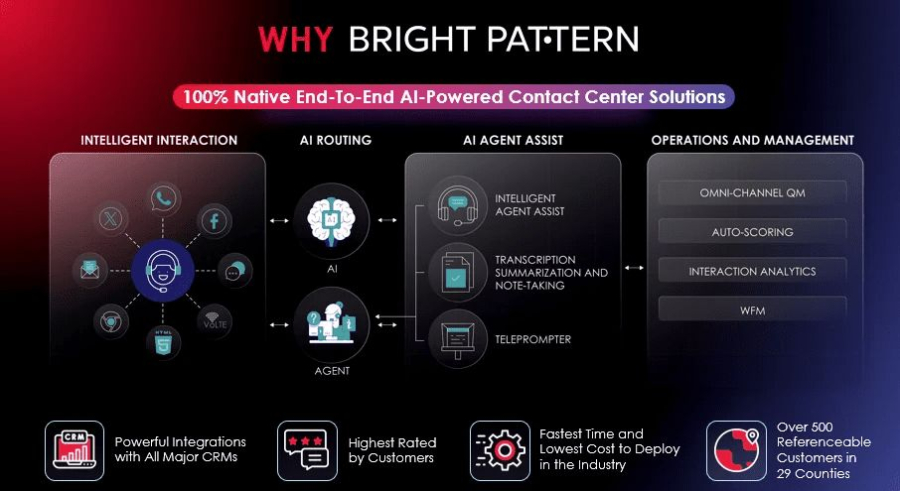
2. NICE inContact – Cloud-Based RPA for Customer Engagement
NICE inContact offers an AI-enhanced platform for automating repetitive contact center tasks, improving call routing, and providing analytics-driven insights to enhance customer satisfaction.
3. Genesys Cloud CX – Intelligent Automation for Omnichannel Support
Genesys combines RPA with AI-powered bots to streamline customer interactions across multiple channels, helping contact centers reduce wait times and optimize agent workloads.
4. Five9 – AI-Powered RPA for Call Center Efficiency
Five9 uses Robotic Process Automation and AI to automate call flows, enhance lead management, and provide agents with real-time guidance during interactions.
5. Twilio Flex – Programmable Contact Center with RPA Integration
Twilio Flex allows contact centers to integrate RPA scripts into workflows, automating routine tasks and connecting seamlessly with AI-driven customer engagement tools.
6. Talkdesk – AI Contact Center Automation for Better CX
Talkdesk leverages RPA for ticket management, voice recognition, and predictive routing, ensuring faster resolutions and improved customer experiences.
7. RingCentral Contact Center – Automated Customer Interactions with AI
RingCentral combines Robotic Process Automation with AI-powered analytics to streamline service operations, optimize agent productivity, and enhance multichannel engagement.
8. 8x8 Contact Center – AI and RPA for Smarter Customer Support
8x8 integrates RPA to automate call flows and reporting, while AI capabilities assist with sentiment analysis and proactive customer engagement.
9. Amazon Connect – Cloud Contact Center Automation with AI
Amazon Connect uses AI-driven RPA to manage routine customer queries, automate IVR processes, and provide intelligent recommendations to agents.
10. Cisco Contact Center – Enterprise RPA and AI Solutions
Cisco provides robust RPA tools combined with AI for large-scale contact centers, enabling workflow automation, predictive analytics, and enhanced agent efficiency.
How RPA Works in Simple Terms
At a high level, RPA tools let you design a series of steps that a software bot should follow. Once created, the bot executes that workflow automatically whenever it is triggered.
Typical RPA workflow
- Trigger: A bot is started by a schedule, an event, or a user command.
- Access: The bot logs into applications or opens web pages.
- Capture: It reads data from screens, files, forms, or emails.
- Process: It applies rules, business logic, and calculations.
- Update: It enters data into systems, generates documents, or sends notifications.
- Log: It records every action for traceability and reporting.
Attended vs. unattended bots
- Attended RPA: Bots run on an employee's desktop and assist in real time. They are triggered by the user and handle parts of the task, speeding up daily work.
- Unattended RPA: Bots run on servers or virtual machines without human intervention. They process work in the background, often 24/7.
The Business Benefits of Robotic Process Automation
RPA is popular because it delivers measurable, tangible benefits across the organization. When deployed thoughtfully, it can quickly pay for itself and continue generating value over time.
1. Major time savings and higher productivity
Bots work faster than humans at simple digital tasks and can run continuously. This leads to:
- Shorter processing timesfor routine work such as invoice handling, data entry, or report generation.
- Faster response to customerswhen used in service or support workflows.
- More throughputwith the same headcount, supporting growth without linear hiring.
2. Improved accuracy and fewer errors
Manual repetitive work often leads to mistakes due to fatigue, distractions, or inconsistent processes. RPA bots follow the same rules every time, which means:
- Fewer data entry errorsand corrections.
- More consistent application of policiesand validation checks.
- Higher quality datafeeding your analytics and reporting.
3. Cost reduction and better use of talent
By offloading repetitive tasks to bots, organizations can:
- Lower the cost per transactionfor high volume processes.
- Avoid or delay new hiresas workloads increase.
- Redeploy employeesfrom low value tasks to higher impact work like customer engagement and analysis.
4. Enhanced compliance and auditability
Many compliance issues come from inconsistent execution of processes. RPA helps by:
- Enforcing standard workflowsacross teams and regions.
- Capturing detailed logsof every step a bot takes.
- Reducing manual handlingof sensitive data, lowering risk.
5. Scalability and flexibility
As your business grows, RPA lets you scale operations without matching that growth with headcount.
- Scale up quicklyby running more bots or allocating more capacity during peaks.
- Adapt processes fasterby updating bot workflows instead of retraining large teams.
- Support seasonal spikesin demand without long term staffing commitments.
6. Better employee experience
Removing repetitive work does not just help the bottom line. It also improves morale and retention:
- Less time on tedious tasksand more time on meaningful work.
- Fewer late nightsduring reporting or closing cycles.
- More capacityfor problem solving, innovation, and customer interaction.
Where RPA Delivers Strong Results: Common Use Cases
RPA is effective anywhere tasks are digital, rules based, and repeatable. Below are popular use cases across core business functions.
Finance and accounting
- Invoice data extraction and posting into ERP systems.
- Accounts payable and receivable processing.
- Bank reconciliation and ledger updates.
- Expense report validation against policies.
- Periodic financial reporting and data consolidation.
Human resources
- Employee onboarding and offboarding checklists.
- HR data entry across payroll, benefits, and HR systems.
- Time and attendance data validation.
- Background check status tracking and notifications.
Customer service and operations
- Automated responses for simple service requests.
- Ticket routing and status updates across systems.
- Order entry and confirmation emails.
- Refund and claim processing with rule based approvals.
IT and shared services
- User account creation, updates, and deprovisioning.
- Password reset workflows with predefined checks.
- System health checks and incident triage.
- Data backups, file transfers, and log collection.
Supply chain and logistics
- Purchase order creation and status updates.
- Inventory level checks and reorder triggers.
- Shipment tracking and customer notifications.
- Carrier rate comparisons based on defined rules.
RPA vs. Traditional Automation vs. AI
RPA is often mentioned alongside automation and artificial intelligence. Understanding the differences helps you choose the right tool for each problem.
Aspect | Manual work | Traditional automation | RPA |
Who performs tasks | Humans | Code in integrated systems | Software bots mimicking users |
Integration requirements | None | APIs and custom development | Works via user interface, minimal integration |
Typical use cases | All tasks | Stable, high volume processes | Screen based, rules driven tasks |
Time to implement | Immediate | Months to years | Weeks to months |
Where AI fits in
Artificial intelligencecomplements RPA by handling tasks that require judgment or pattern recognition. For example, AI can classify emails or interpret unstructured documents, while RPA handles the structured steps that follow. Together, they enable more advanced, end to end automation.
Is Your Process a Good Fit for RPA?
Not every task is ideal for RPA. The strongest candidates share several characteristics.
Good candidates for RPA
- High volume: Performed many times each day, week, or month.
- Rule driven: Clear, stable rules with limited exceptions.
- Digital and structured: Data is accessible in electronic form.
- Low variation: Few process paths, with predictable steps.
- System heavy: Involves multiple applications or data transfers.
Examples of strong RPA candidates
- Transferring order data from emails into an order management system.
- Validating customer information between CRM and billing systems.
- Generating standard weekly or monthly reports from multiple data sources.
Step by Step: How to Implement RPA Successfully
A structured approach helps you realize value quickly and avoid common pitfalls. Below is a practical roadmap.
1. Identify and prioritize use cases
- Engage managers and frontline employees to list time consuming tasks.
- Score each process on volume, complexity, and business impact.
- Select a small number of high impact, low complexity candidates for initial pilots.
2. Analyze and standardize the process
- Document each step, decision point, and exception path.
- Eliminate unnecessary steps before automating.
- Agree on a single, standardized way of working as the basis for the bot.
3. Design and build the bot workflow
- Use your RPA platform's visual designer to map steps and rules.
- Define how the bot will handle exceptions or missing data.
- Include logging, alerts, and basic monitoring from the start.
4. Test thoroughly with real scenarios
- Run the bot in a test environment using real data samples.
- Validate accuracy, speed, and exception handling.
- Involve business users to confirm the output meets their needs.
5. Deploy, monitor, and refine
- Roll out the bot in phases, starting with limited volumes if needed.
- Monitor performance, error rates, and user feedback.
- Continuously fine tune rules and expand coverage to more scenarios.
6. Scale across the organization
- Establish an automation roadmap aligning with business priorities.
- Create standards, templates, and governance for consistent rollouts.
- Share success stories internally to build momentum and adoption.
Measuring the Impact of RPA
To build a strong business case and refine your automation strategy, it is essential to measure results. Clear metrics help you demonstrate value and target new opportunities.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) for RPA
- Time savedper transaction or per employee.
- Throughput: Number of items processed per hour or per day.
- Error rate reductioncompared to manual processing.
- Cost savingsfrom reduced manual effort and rework.
- Cycle timefrom task initiation to completion.
- Employee satisfactionscores in automated teams.
Example of a simple RPA benefit calculation
Manual effort per task: 10 minutes
Tasks per month: 5,000
Total manual hours per month: 10 * 5,000 / 60 = 833 hours If a bot completes each task in 2 minutes of processing time:
Automated hours per month: 2 * 5,000 / 60 = 167 hours Approximate time saved: 666 hours per month
Even after accounting for bot licenses and maintenance, the combination of time savings and error reduction often results in a strong return on investment.
Best Practices for Sustainable RPA Success
Organizations that see lasting value from RPA treat it as a strategic capability, not just a one off project.
1. Start small, but think big
- Use early pilots to prove value quickly and build internal support.
- Design your governance, standards, and architecture with future expansion in mind.
2. Involve both business and IT
- Business teams understand the process details and pain points.
- IT teams ensure security, reliability, and alignment with technical standards.
- Joint ownership reduces bottlenecks and improves solution quality.
3. Keep processes clean and stable
- Review and optimize workflows before you automate them.
- Limit frequent process changes that would require constant bot updates.
- Document decisions so future teams can maintain and enhance bots easily.
4. Plan for maintenance and governance
- Assign clear ownership for each bot and its performance.
- Set up monitoring to catch issues quickly and minimize downtime.
- Review your RPA portfolio regularly to retire low value automations and focus on the best opportunities.
5. Invest in skills and change management
- Train power users and analysts to identify and design automation candidates.
- Communicate transparently with employees about how RPA supports their work.
- Highlight success stories where automation freed teams to focus on strategic tasks.
The Future of Robotic Process Automation
RPA is evolving rapidly and is increasingly combined with other technologies to create more powerful automation solutions.
Emerging directions
- Intelligent automation: Combining RPA with AI and machine learning for smarter decision making and handling of unstructured data.
- Process mining: Using system logs to discover, analyze, and prioritize processes for automation.
- Citizen development: Empowering non technical users to build and manage simple automations, under governance.
- End to end digital workflows: Integrating RPA with workflow tools and APIs to automate entire journeys, not just individual tasks.
As these capabilities mature, organizations that invest early and build strong automation practices can expect compounding benefits in efficiency, quality, and agility.
Bringing It All Together
Robotic Process Automation offers a practical, high impact way to modernize operations without tearing out your existing systems. By targeting repetitive, rules based tasks, RPA delivers faster processing, greater accuracy, lower costs, and a better employee experience.
With a focused strategy, strong collaboration between business and IT, and a commitment to continuous improvement, RPA can become a core capability that supports growth, resilience, and innovation across your organization.
